This drawing was a breakthrough for me in understanding the major overarching functional organization of the brain: the Thalamus mediates Nexus formation in the adjacent ventricles where ‘raw’ sensory inputs are first presented to consciousness. That happens because ALL sensory inputs, with the single exception of olfaction (sense of smell) first go to the thalamus, at the top of the brainstem. The thalamus then relays those sensory inputs upward to cerebral cortex for interpretation, and the interpreted information is sent from cortex back down to the thalamus where it is integrated with the raw signals in consciousness to provide meaning to experience. The mapping shows how the visual inputs for example first reach the thalamus at V1 (the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus) and then the visual signals are relayed to the V1 area of cerebral cortex at the back of the brain. Interpretation of visual signals in cortex occurs in the surrounding visual association areas (VA) and is then returned to the VA area of the thalamus.
Incidentally, an important clue helping to inform us that consciousness is not occurring in cerebral cortex is that the amount of interpreted information (in terms of neural traffic) the cerebral cortex returns back to the thalamus is about ten times more than the sensory information thalamus relays to cortex!
I recommend that you print this image (right-click on it below to download at 627 x 565 resolution) and tape it to your bathroom wall where you can study it frequently until it makes sense to you. This adaptation of Newman’s map was the breakthrough for me in understanding the layout of the brain, showing the ‘mapping’ between cerebral cortex and the thalamus.
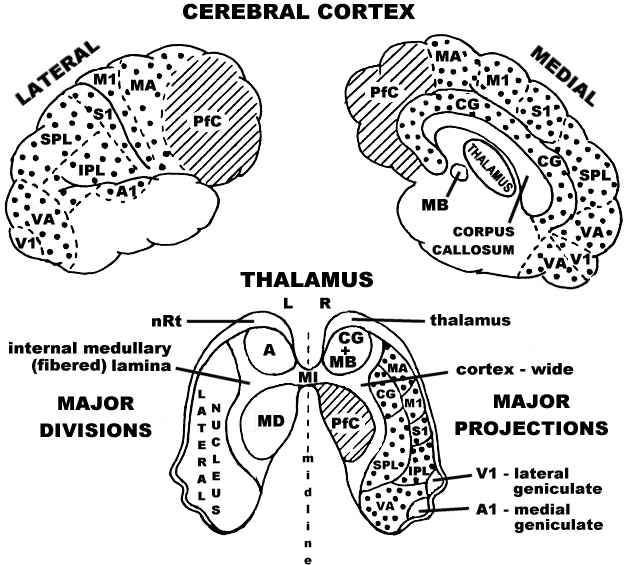
The major divisions of the thalamus and the major projections it shares with the cerebral cortex
(Adapted from Newman, 1995).
Major thalamic nuclei are labeled on the left side:
- A – anterior nucleus
- MD – medialdorsal nucleus
- MI – massa intermedia
- nRt – nucleus reticularis thalami (where the ‘gating’ control of incoming signals occurs)
Thalamocortical projection areas and corticothalamic reception areas of the thalamus are labeled on the right and map to their correspondingly labeled areas on cortex:
- A1 – primary auditory cortex
- CG – cingulate gyrus
- IPL – inferior parietal lobule
- M1 – primary motor cortex
- MA – motor association cortex
- MB – mammilary body
- PfC – prefrontal cortex
- S1 – primary somatosensory cortex
- SPL – superior parietal lobule
- V1 – primary visual cortex
- VA – visual association cortex
